We are working with some very cool partners in emerging and innovative technologies.
Defensive Security
The CISO is at the center of Defensive Strategy. A defensive strategy can aid in developing new strategies for the future. Defensive strategies are developed to protect the current market share but if a company can identify how competitors are attacking them, they can incorporate the same strategy into their own plans and in doing so; the company can ensure that they are not left behind by its competitors.
A layered defensive strategy can protect market share and increase profitability at the same time. The advantage of having a low cost structure compared to that of a competitor means that a company can use defensive strategies to protect its market share and at the same time, increase profitability.
Innovation
Market Changing Innovation often referred to as a “game-changer” can refer to a person who is a visionary or a company that alters its business strategy and conceives an entirely new business plan – defining a new market. This type of company provides a new business strategy in order to compete directly or indirectly with competitors. A market-changer changes the way that something is done, thought about, or made. While achieving game-changing levels this is typically a long-term achievement that takes time, determination, and the ability to ride out the uncertainties that you or your company will face along the way.
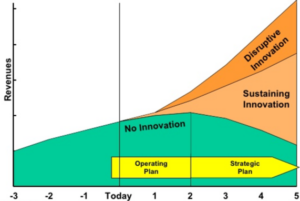
Disruptive and Sustaining Innovation these are the common and fast moving innovations that come to market quickly to change a markets character. This why the market changing technology has to keep a watchful eye on the markets as they tend to creep toward there newly defined markets.

Sustaining Innovation does not create new markets but rather only evolves existing ones with better value. Allowing the firms within to compete against each other’s sustaining improvements. They are developed by established companies often seen as a leaders or challengers in the market. Adding a new feature to an existing solution that offers a slight advantage, is an example of a sustained innovation – termed “leap-frogging”.
Disruptive Innovation is an innovation that disrupts an existing market, innovations that improve a product or service in ways that the market does not expect that infringes on current customer value – termed “quantum leap”. Products based on Disruptive technologies are typically cheaper to produce, simpler, smaller, better performing, and, frequently, more convenient to use.
Cleantech
The definition of cleantech is any product or service that improves operational performance, productivity, or efficiency while reducing costs, inputs, energy consumption, waste, or environmental pollution.
Environmental finance is a method by which new clean technology projects that have proven that they are “additional” or “beyond business as usual” can obtain financing through the generation of carbon credits.
Environmental Impact of Clean Technology
Minimizing the environmental impact all comes down to infrastructure agility, space, power, cooling and the challenges of efficiency without impacting operations. Optimization of power usage efficiency (PUE) means if managed and controlled their is less carbon footprint. This is mandatory and is a major part of the journey of resiliency, density and effectiveness. In collaboration with the electricity sector, its stakeholders, and others our intent is to reduce the dependence on electrical power, increase the reliability of its usage making it affordable, and environmentally responsible:
- Utilize minimal resources
- Operate with high efficiency
- Reduce and reclaim energy
- Operate with a low CO2 footprint
- Positively impact the environment
- Create Carbon-Neutral tax credits
Cleantech Strategic Effects
How Gartner Identifies Strategic Technologies
Gartner defines a strategic market changing technology trend as one with the potential for significant impact on the industry as a whole. Factors that denote significant impact include a high potential for disruption to the business, end users, the need for a major investment, or the risk of being late to adopt and how fast this innovation spreads through the culture. These technologies generate significant new value and impact the organization’s long-term plans, programs and initiatives.

